Chapter 1
Concepts of Governance and Management of Information Systems
PART 3
As we have already discussed about basics of governance. Now this is time to understand one of the most important topic of this chapter. COBIT 5.
Control objectives for information and related technology (COBIT 5). It is developed by "Information System Audit and Control Association" (ISACA), USA.
What is COBIT 5. ( This para is for basic understanding of term)
Why and Purpose?
Its purpose is Shareholders value creation and goal achievement.
How?
Through good governance and management of IT assets.
Why of IT Assets?
Delivering enterprise stakeholders value requires good governance and management of IT assets.
Therefore, enterprise board, executive and management have to embrace IT like any other significant part of the business.
COBIT 5 is a Governance as well as Management model.
Under governance comes
* Evaluation
* Direction Setting
* Monitoring
Think Like what our PM is doing right now? He is doing all above.
On the other hand, Management plans, builds, runs and monitor activities in alignment with the direction set by the governance body to achieve the enterprise objectives.
So what will COBIT 5 do?
It provides a comprehensive framework that assist enterprises to achieve their goal and deliver value through effective governance and management of enterprise IT.
Simply stated, COBIT 5 helps enterprises create optimal value from IT by maintaining a balance b/w realizing benefits, optimal risk level, resource use and their cost.
Definition of COBIT 5
COBIT 5 brings together the 5 principles that allow the enterprise to build an effective governance and management framework based on holistic set of seven enablers ( framework is based on seven enablers but framework is build by using 5 principles) that optimizes information and technology investment and use for benefit of shareholders.
What are the 5 Principles?
We will discuss each one by one?
PRINCIPLE NO. 1
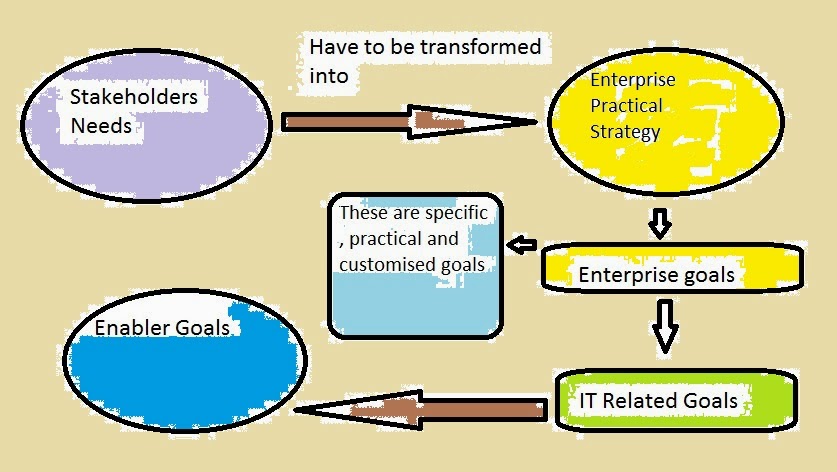
MEETING STAKEHOLDERS NEEDS
As we all know, Enterprise exist for delivering value to stakeholders and governance objective is also value creation for stakeholders.
Value creation = What Stakeholders need?
Therefore, Stakeholders needs drive
*Business Realization
*Risk Optimization
*Resource Optimization
Enterprise have many stakeholders and 'Creating Value' means different and sometimes conflicting things to each of them.
Take for example, sometimes owners want to retain profit made in the business but on the other hand shareholders want dividend. Therefore needs of both of them are different plus they are also conflicting.
Therefore, Governance is also about negotiating and deciding among different stakeholders value interest. The Governance system should consider all stakeholders when making benefit, resource and risk assessment decision.
For each decision following can and should be asked
* Who receives the benefit?
* Who bears the risk?
* What resources are required.
Other Principles is in Next Post.................
CA Mohit Jain
Ph; 08053881595
Email: camohitjain7@gmail.com
Comments
Post a Comment